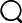How is the metallization layer applied to Metallized BOPP Film during production?
Metallized BOPP film is a widely used material in the packaging industry, known for its excellent barrier properties, aesthetic appeal, and versatility in various applications. The process of applying the metallization layer is critical in determining the performance, appearance, and durability of the final product.
Overview of Metallized BOPP Film
Metallized BOPP film is a biaxially oriented polypropylene (BOPP) film that has undergone a surface coating process with a thin metal layer, typically aluminum. The metallization enhances the film’s barrier properties against moisture, oxygen, and light, while also providing a reflective, glossy finish suitable for packaging and decorative applications. Metallized BOPP film is extensively used in food packaging, snack wrappers, labels, and other consumer goods packaging due to its combination of flexibility, printability, and durability.
The production quality of metallized BOPP film is largely determined by the uniformity and adhesion of the metallization layer. Therefore, understanding how the metallization layer is applied is crucial for evaluating product performance and selecting the right material for specific applications.
Production Process of Metallized BOPP Film
The production of metallized BOPP film involves multiple stages, including substrate preparation, metallization, post-treatment, and quality control. Each stage requires careful management to ensure consistent properties across the film.
Substrate Preparation
Before metallization, the BOPP film must be properly prepared to ensure strong adhesion of the metal layer. This preparation typically involves:
-
Surface Treatment: BOPP film has a low surface energy, which can hinder the adhesion of metal layers. A common method to enhance surface energy is corona treatment or plasma treatment. This process modifies the film surface, making it more receptive to metallization and coating materials.
-
Cleaning: Any dust, debris, or surface contamination on the BOPP film can create defects in the metallization layer. The film is carefully cleaned using air knives or rollers to remove particles before entering the metallization chamber.
Proper substrate preparation is essential to prevent defects such as peeling, uneven coating, or pinholes in the metallized layer.
Metallization Techniques
The application of the metallization layer can be performed using various techniques, but the most commonly used method in the production of metallized BOPP film is vacuum metallization. This process ensures a uniform, thin, and durable metal layer.
Vacuum Metallization Process
Vacuum metallization is a physical vapor deposition (PVD) technique that deposits a thin layer of metal, usually aluminum, onto the BOPP film surface under controlled vacuum conditions. The process includes the following key steps:
-
Film Loading: The prepared BOPP film is unwound from rolls and passed through a metallization chamber. The chamber is designed to maintain a high vacuum, reducing the presence of air molecules that can interfere with metal deposition.
-
Metal Evaporation: In the vacuum chamber, the metal source is heated to a temperature high enough to cause evaporation. For aluminum, this is achieved using resistance heating or electron beam heating. The evaporated metal particles travel in a straight path and condense onto the surface of the BOPP film.
-
Deposition Control: The thickness and uniformity of the metal layer are controlled by adjusting the deposition rate, distance between the metal source and film, and film speed. Typical aluminum layers on BOPP film range from 8 to 15 nanometers, providing effective barrier properties without compromising flexibility.
-
Cooling and Stabilization: After deposition, the metallized film is gradually cooled to prevent thermal stress and maintain dimensional stability. The film is then rolled onto take-up rolls for further processing.
Vacuum metallization is preferred for Metallized BOPP Film due to its ability to produce a highly reflective surface, excellent barrier properties, and uniform layer distribution.
Post-Treatment Processes
After metallization, the film may undergo additional treatments to enhance performance and durability:
-
Protective Coating: A thin coating of lacquer or polymer can be applied over the metallized layer to improve scratch resistance, chemical resistance, and printability. This protective coating is particularly important for packaging applications where the film may be subjected to handling, folding, or heat sealing.
-
Heat Treatment: Some manufacturers perform a controlled heat treatment to stabilize the metallized layer and reduce the risk of peeling during subsequent processing.
-
Slitting and Rewinding: The metallized BOPP film is slit into rolls of desired width and rewound with care to prevent surface damage. Proper tension control during rewinding ensures smooth rolls and uniform film thickness.
Quality Control and Inspection
Quality control is a critical step in the production of metallized BOPP film. The metallization layer must meet strict specifications for adhesion, thickness, and barrier performance. Common inspection methods include:
- Visual Inspection: Detects defects such as pinholes, streaks, or uneven coating.
- Adhesion Tests: Measures the bond strength between the metal layer and BOPP substrate.
- Barrier Property Testing: Evaluates moisture vapor transmission rate (MVTR) and oxygen transmission rate (OTR).
- Gloss and Reflectivity Measurement: Ensures the film meets aesthetic requirements for packaging and decorative applications.
Consistent quality control ensures that Metallized BOPP Film meets the expectations of buyers in industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods.
Applications and Advantages of Metallized BOPP Film
The application of the metallization layer greatly influences the functional properties of BOPP film. Metallized BOPP film offers several advantages that make it an attractive choice in the packaging industry:
- Barrier Protection: The metallized layer significantly reduces the transmission of light, oxygen, and moisture, protecting sensitive products from spoilage.
- Aesthetic Appeal: The reflective surface enhances product presentation, making it ideal for luxury packaging and promotional materials.
- Printability: Post-treatment coatings improve ink adhesion, allowing high-quality printing and branding.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to metal foil laminates, metallized BOPP film provides similar barrier performance at a lower weight and cost.
Applications include snack and confectionery wrappers, coffee packaging, labels, decorative packaging, and lamination for composite structures.
Industry Considerations for Buyers
When selecting Metallized BOPP Film, buyers should consider several technical and operational factors:
- Layer Thickness: The thickness of the metallization layer affects barrier performance and reflectivity. Buyers should match specifications to the requirements of the packaged product.
- Surface Treatment: Adequate corona treatment is essential for printing, laminating, or coating.
- Roll Quality: Uniform tension and defect-free rolls prevent production issues during downstream processing.
- Barrier Performance: MVTR and OTR values must meet industry standards, particularly for sensitive food and pharmaceutical products.
- Sustainability: Some buyers consider recyclability and environmental impact when selecting metallized films.
By evaluating these aspects, buyers can ensure that the selected Metallized BOPP Film meets both functional and aesthetic requirements.
Table: Summary of Metallization Process
| Stage | Key Steps | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Substrate Preparation | Cleaning, corona treatment | Improve adhesion of metal layer |
| Metallization | Vacuum deposition of aluminum | Apply uniform barrier layer |
| Post-Treatment | Protective coating, heat stabilization | Enhance durability and printability |
| Quality Control | Visual inspection, adhesion tests, barrier tests | Ensure consistent product performance |
Conclusion
The application of the metallization layer is a complex but essential step in producing high-quality metallized BOPP film. From substrate preparation to vacuum deposition, post-treatment, and rigorous quality control, each stage contributes to the film’s barrier properties, visual appeal, and durability. Understanding the production process allows manufacturers to optimize performance and helps buyers select the right material for their packaging needs.
As industries continue to demand high-performance, visually appealing, and cost-effective packaging solutions, metallized BOPP film remains a versatile and reliable choice. Knowledge of the metallization process enables informed decisions that balance functionality, aesthetics, and production efficiency.


 English
English  中文简体
中文简体